前提
安装wiringPi
阅读《OrangePi_Zero_H2+_用户手册_v3.2.pdf》“3.20. 26 Pin 接口引脚说明”章节,按照说明进行安装。 当前情况下安装后发现执行会报错:
root@orangepi:~# apt update
root@orangepi:~# apt install git
root@orangepi:~# git clone https://github.com/orangepi-xunlong/wiringOP
root@orangepi:~# cd wiringOP
root@orangepi:~/wiringOP# ./build clean
root@orangepi:~/wiringOP# ./build
# 报错
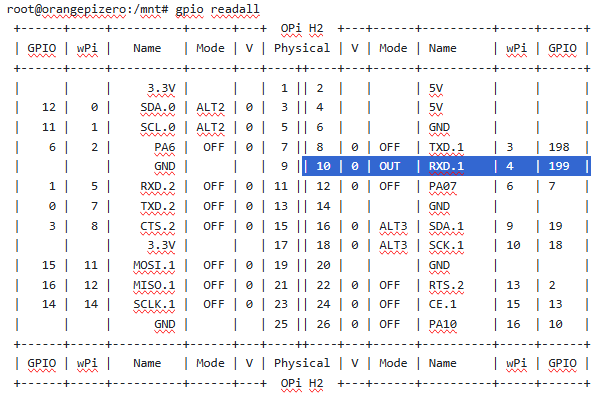
root@orangepi:~# gpio readall
root@orangepi:~# wiringPiSetup: mmap (PWM) failed: Invalid argument原因:orangepi官方代码问题,参见:
https://github.com/orangepi-xunlong/wiringOP/issues/96 git checkout -b a846ffd8f5583516cd25c6b08e49fd9cc47728c4 我测试这个编译也不行。然后再切回master才行不知为何。
#按照issue说明切到改提交点
root@orangepizero:/mnt# git checkout -b a846ffd8f5583516cd25c6b08e49fd9cc47728c4
./build clean
./build
#不知为何以上自己build后还不能用,再切回来build才行。 如果不行多切几次..
root@orangepizero:/mnt# git checkout master
./build clean
./buildgpio引脚图
root@orangepizero:/mnt# gpio readall
+------+-----+----------+------+---+ OPi H2 +---+------+----------+-----+------+
| GPIO | wPi | Name | Mode | V | Physical | V | Mode | Name | wPi | GPIO |
+------+-----+----------+------+---+----++----+---+------+----------+-----+------+
| | | 3.3V | | | 1 || 2 | | | 5V | | |
| 12 | 0 | SDA.0 | ALT2 | 0 | 3 || 4 | | | 5V | | |
| 11 | 1 | SCL.0 | ALT2 | 0 | 5 || 6 | | | GND | | |
| 6 | 2 | PA6 | OFF | 0 | 7 || 8 | 0 | OFF | TXD.1 | 3 | 198 |
| | | GND | | | 9 || 10 | 0 | OUT | RXD.1 | 4 | 199 |
| 1 | 5 | RXD.2 | OFF | 0 | 11 || 12 | 0 | OFF | PA07 | 6 | 7 |
| 0 | 7 | TXD.2 | OFF | 0 | 13 || 14 | | | GND | | |
| 3 | 8 | CTS.2 | OFF | 0 | 15 || 16 | 0 | ALT3 | SDA.1 | 9 | 19 |
| | | 3.3V | | | 17 || 18 | 0 | ALT3 | SCK.1 | 10 | 18 |
| 15 | 11 | MOSI.1 | OFF | 0 | 19 || 20 | | | GND | | |
| 16 | 12 | MISO.1 | OFF | 0 | 21 || 22 | 0 | OFF | RTS.2 | 13 | 2 |
| 14 | 14 | SCLK.1 | OFF | 0 | 23 || 24 | 0 | OFF | CE.1 | 15 | 13 |
| | | GND | | | 25 || 26 | 0 | OFF | PA10 | 16 | 10 |
+------+-----+----------+------+---+----++----+---+------+----------+-----+------+
| GPIO | wPi | Name | Mode | V | Physical | V | Mode | Name | wPi | GPIO |
+------+-----+----------+------+---+ OPi H2 +---+------+----------+-----+------+风扇
OrangePi Zero只贴了一个散热片,在20多度的室温下运行PiKVM情况下CPU温度有50°C左右,有点高所以需要添加一个风扇。刚好它有很多GPIO口。因此做一个可启停的风扇当温度高于50°C时启动风扇。
虽然OrangePi Zero支持PWM调速但是风扇比较羸弱转速也不快也就不需要调速了,直接全速降温。
准备
风扇小于5CM * 5CM的风扇
1K电阻
杜邦线若干
S8050 三极管或其他

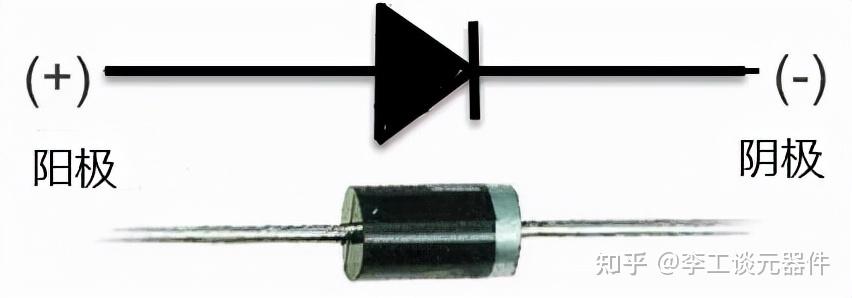
二极管(如1N4007)
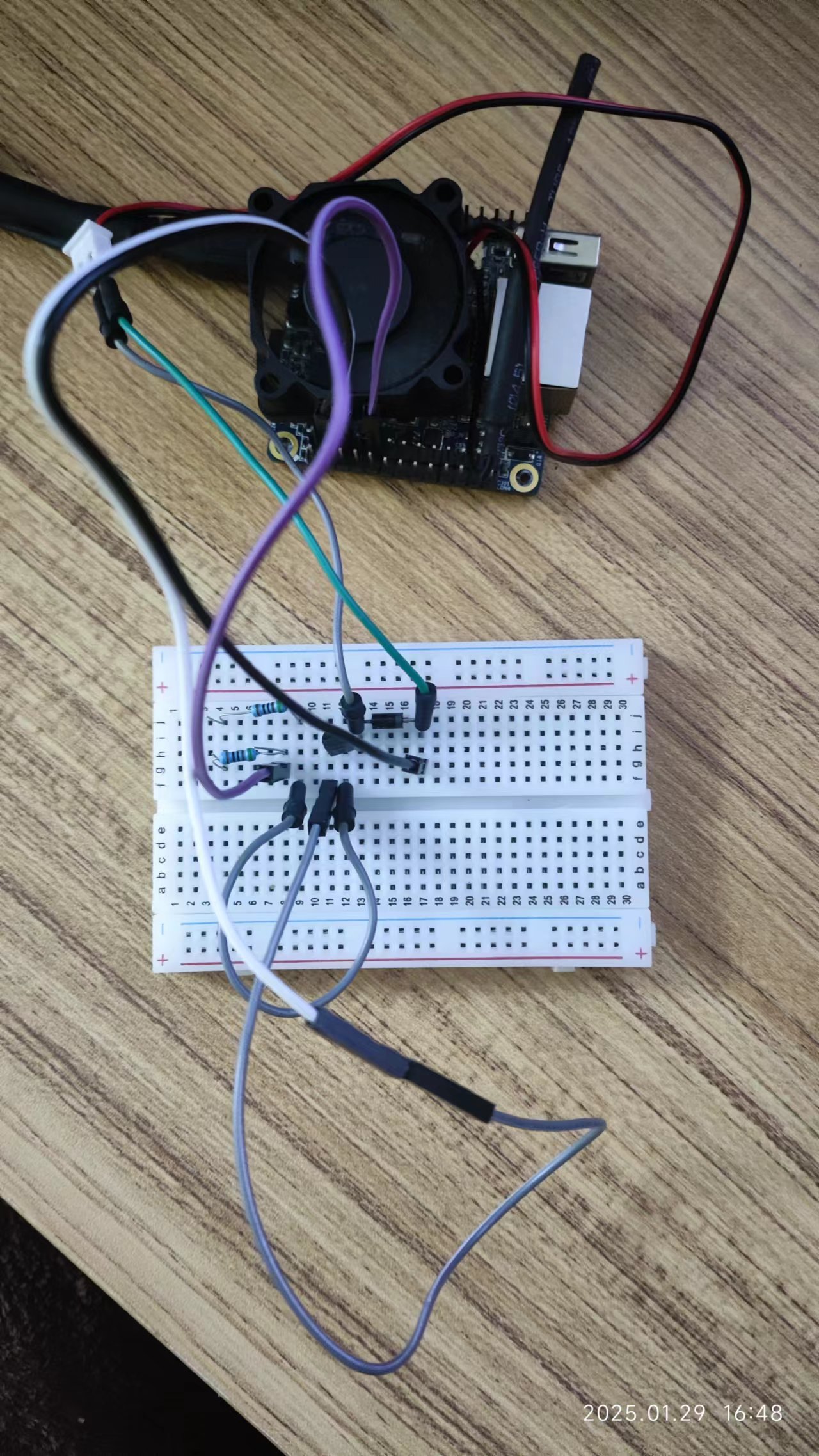
接线示意
这里使用使用wPi=4来进行控制,物理引脚为10
Orange Pi Zero 外部电路
+------------------+ +-----------------+
| GPIO (wPi=4) |----[1kΩ]----| B (晶体管基极) |
| 5V (引脚4) |----------------| + (风扇正极) |
| GND (引脚6) |----------------| - (风扇负极) |
+------------------+ | E (晶体管发射极) |
| C (晶体管集电极)--+--> 风扇负极
+-----------------+
二极管反向并联在风扇两端接线步骤
风扇正极 → 直接连接到 Orange Pi 的 5V 引脚(物理引脚4)。
风扇负极 → 连接到 晶体管集电极(C)。
晶体管发射极(E) → 连接到 Orange Pi 的 GND 引脚(物理引脚6)。
GPIO(wPi=4) → 通过 1kΩ 电阻 连接到 晶体管基极(B)。
二极管 → 反向并联在风扇两端(阴极接风扇正极,阳极接风扇负极)。
示例图
测试
gpio mode 4 out
#测试风扇是否启动
gpio write 4 1
#关闭风扇
gpio write 4 0脚本
nano /usr/local/bin/fan.sh
#!/bin/bash
# 控制是否输出调试信息到控制台: 1为启用, 0为禁用
DEBUG=1
# 温度阈值(单位℃)
TEMP_THRESHOLD_ON=50 # 开启风扇的温度阈值
FAN_PIN=4 # 假设风扇连接在GPIO引脚4上
gpio mode $FAN_PIN out #确保引脚为输出状态
COOL_DOWN_PERIOD=120 # 冷却时间(秒),即温度低于阈值后等待2分钟再关闭风扇
debug_echo() {
# 如果启用了调试模式,则输出传递给函数的信息
if [ "$DEBUG" -eq 1 ]; then
echo "$@"
fi
}
# 初始化冷却计时器为冷却周期
cool_down_timer=$COOL_DOWN_PERIOD
RUNNING=true
fun() {
while $RUNNING; do
# 获取CPU温度并转换为摄氏度
CPU_TEMP=$(cat /sys/class/thermal/thermal_zone0/temp | awk '{print $1/1000}')
# 使用自定义的debug_echo函数输出当前时间和获取的CPU温度
debug_echo "$(date '+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S') - 当前CPU温度: ${CPU_TEMP}℃"
if (( $(echo "$CPU_TEMP > $TEMP_THRESHOLD_ON" | bc -l) )); then
# 如果温度高于阈值,开启风扇并重置冷却计时器为冷却周期
gpio write $FAN_PIN 1
cool_down_timer=$COOL_DOWN_PERIOD # 重置冷却计时器
debug_echo "$(date '+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S') - 温度超过阈值($TEMP_THRESHOLD_ON℃),开启风扇."
else
# 如果温度低于阈值,检查冷却计时器是否达到设定的时间
if [ $cool_down_timer -le 0 ]; then
# 如果冷却计时器已归零或小于等于0,关闭风扇
gpio write $FAN_PIN 0
debug_echo "$(date '+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S') - 温度低于阈值($TEMP_THRESHOLD_ON℃),并且冷却计时器已结束,关闭风扇."
else
# 如果冷却计时器尚未达到设定时间,继续等待,并递减冷却计时器
debug_echo "$(date '+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S') - 等待冷却计时器倒计时: ${cool_down_timer}s"
cool_down_timer=$((cool_down_timer - 30))
fi
fi
# 等待30秒后再次检查
sleep 30
done
}
case "$1" in
start)
echo "启动风扇..."
fun
;;
stop)
echo "关闭风扇..."
RUNNING=false
;;
*)
echo "用法: $0 {start|stop}"
exit 1
;;
esac
exit 0自启动服务
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/fan.sh
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/fan-control.service
```
[Unit]
Description=Fan Control Service
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=simple
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/fan.sh start
ExecStop=/usr/local/bin/fan.sh stop
Restart=on-failure
StandardOutput=journal
StandardError=inherit
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
```
# 重新加载systemd配置
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
# 启用开机自启
sudo systemctl enable fan-control.service
# 立即启动服务
sudo systemctl start fan-control.service
# 查看服务状态
sudo systemctl status fan-control.service加电开启风扇
说明:以上再进入内核后才会检测风扇开启状态,要在板子加电就开启风扇需要一下设置
方法:
修改DTB文件,对应引脚的定义
修改Uboot源码
再Uboot启动时设置对应引脚为高电平
这里使用方法3,方便一些: 接上TTL, 启动时按空格进入Uboot环境输入以下:
#uboot启动时按空格进入设置uboot env
setenv bootcmd 'gpio set 199; run distro_bootcmd'
saveenv
#重启uboot
resetLED屏幕显示
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43288375/article/details/131148818
准备
0.96 OLED 1315 显示屏 (5V)
杜邦线若干
前提
阅读《OrangePi_Zero_H2+_用户手册_v3.2.pdf》“3.22.3. I2C ”章节 开启I2C
#挂载boot分区
mount /dev/mmcblk0p1 /mnt
#nano /mnt/armbianEnv.txt 最后添加:
overlays=i2c0 i2c1
#重启板子
reboot阅读《OrangePi_Zero_H2+_用户手册_v3.2.pdf》“3.23. I2C 接口的 0.96 寸 寸 OLED ”章节,按照说明进行安装必要组件。并测试
apt update
apt install i2c-tools -y
i2cdetect -y 0
#显示一下说明正常:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f
00: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
10: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
20: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
30: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 3c -- -- --
40: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
50: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
60: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
70: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 示意图
安装软件
#全局安装
sudo pip3 install adafruit-circuitpython-ssd1306 --break-system-packages
sudo pip3 install psutil --break-system-packages
sudo pip3 install Pillow --break-system-packages 脚本
说明:脚本来自:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43288375/article/details/131148818 新增了亮度控制,默认太亮了
#编写脚本
nano /usr/local/bin/oled.py
import time
import shutil
import subprocess
import psutil
import board
import digitalio
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont
import adafruit_ssd1306
from datetime import datetime
# 定义屏幕尺寸
WIDTH = 128
HEIGHT = 64
BORDER = 5
# 全局资源初始化
i2c = None
oled = None
def cleanup(signum=None, frame=None):
"""清理资源:关闭屏幕并释放 GPIO"""
global oled, i2c
if oled:
oled.fill(0)
oled.show()
print("Screen cleared on exit.")
if i2c:
i2c.deinit() # 释放 I2C 总线资源
sys.exit(0)
def init_display():
"""初始化 OLED 屏幕"""
global i2c, oled
try:
i2c = board.I2C()
oled = adafruit_ssd1306.SSD1306_I2C(WIDTH, HEIGHT, i2c)
oled.contrast(10) # 初始对比度
oled.fill(0)
oled.show()
print("OLED initialized.")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Display init failed: {str(e)}")
cleanup()
# 注册退出信号(Ctrl+C 或 systemd 停止)
signal.signal(signal.SIGINT, cleanup)
signal.signal(signal.SIGTERM, cleanup)
def set_contrast(level):
"""
设置屏幕对比度(亮度)
:param level: 对比度级别 (0-255)
"""
oled.contrast(level)
def get_disk_usage():
total, used, free = shutil.disk_usage("/")
disk_space = used / (2**30) # 转换为GB
disk_percent = (used / total) * 100 # 计算已用硬盘空间百分比
return disk_space, disk_percent
def get_memory_usage():
mem = psutil.virtual_memory()
memory_usage = mem.used / (2**30) # 转换为GB
memory_percent = (mem.used / mem.total) * 100 # 计算已用内存空间百分比
return memory_usage, memory_percent
def get_cpu_usage():
# 获取所有核心的平均使用率
cpu_usage = psutil.cpu_percent(interval=1)
# 获取每个核心的使用率
cpu_usage_per_core = psutil.cpu_percent(interval=None, percpu=True)
cpu_usage_per_core_int = [int(core_usage) for core_usage in cpu_usage_per_core]
# 格式化核心使用率为 "1% / 2%"
p_core_usages = "/".join([f"{usage}" for usage in cpu_usage_per_core_int])
return cpu_usage,p_core_usages
def get_cpu_temperature():
temperature = subprocess.check_output(["cat", "/sys/class/thermal/thermal_zone0/temp"]).decode("utf-8")
cpu_temp = float(temperature) / 1000
return cpu_temp
def get_ip_address():
ip_address = subprocess.check_output(["hostname", "-I"]).decode("utf-8").split(" ")[0]
return ip_address
def main_loop():
"""主显示循环"""
try:
# 创建图像对象
image = Image.new("1", (WIDTH, HEIGHT))
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image)
font = ImageFont.load_default()
while True:
draw.rectangle((0, 0, WIDTH, HEIGHT), outline=0, fill=0) # 清空画布
# 获取系统数据(添加异常处理)
try:
disk_space, disk_percent = get_disk_usage()
memory_usage, memory_percent = get_memory_usage()
cpu_temperature = get_cpu_temperature()
ip_address = get_ip_address()
cpu_usage, p_cpu_usages = get_cpu_usage()
except Exception as e:
print(f"Data read error: {str(e)}")
draw.text((BORDER, 0), "Data Error!", font=font, fill=255)
oled.image(image)
oled.show()
time.sleep(5)
continue
# 更新显示内容(优化布局)
y_pos = 0
draw.text((BORDER, y_pos), f"Disk: {disk_space:.1f}G ({disk_percent:.1f}%)", font=font, fill=255)
y_pos += 10
draw.text((BORDER, y_pos), f"RAM: {memory_usage:.1f}G ({memory_percent:.1f}%)", font=font, fill=255)
y_pos += 10
draw.text((BORDER, y_pos), f"CPU: {cpu_usage}% ({p_cpu_usages})", font=font, fill=255)
y_pos += 10
draw.text((BORDER, y_pos), f"Temp: {cpu_temperature:.1f}°C", font=font, fill=255)
y_pos += 10
draw.text((BORDER, y_pos), f"IP: {ip_address}", font=font, fill=255)
# 更新屏幕
oled.image(image)
oled.show()
time.sleep(3) # 可调整刷新间隔
except Exception as e:
print(f"Main loop error: {str(e)}")
cleanup()
if __name__ == "__main__":
init_display()
main_loop()自启动服务
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/oled-control.service
```
[Unit]
Description=OLED Control Service
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=simple
ExecStart=python3 /usr/local/bin/oled.py
Restart=on-failure
StandardOutput=journal
StandardError=inherit
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
```
# 重新加载systemd配置
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
# 启用开机自启
sudo systemctl enable oled-control.service
# 立即启动服务
sudo systemctl start oled-control.service
# 查看服务状态
sudo systemctl status oled-control.service关机
关机时关闭风扇和oled显示屏
nano /etc/systemd/system/poweroff.service
[Unit]
Description=Shutdown OLED Display
DefaultDependencies=no
Before=poweroff.target halt.target
After=sysinit.target
[Service]
Type=oneshot
RemainAfterExit=yes
ExecStop=/usr/local/bin/gpio write 4 0 # 停止风扇
ExecStop=/usr/sbin/i2cset -y 0 0x3C 0x00 0xAE # 关闭屏幕命令(SSD1306)
[Install]
WantedBy=poweroff.target完工


评论区